A browser or search engine crawler sends an HTTP request to fetch a page. The response code indicates the page’s status. There is a lengthy list of HTTP status codes, and each one specifies a different set of circumstances. In this blog post, we will describe the distinction between 404 and soft 404 errors. Read on to find out!
What is Error 404?
A 404 error meaning or status code indicates that the requested Web page could not be located or is no longer accessible.
Generally, a 404 error happens when:
An error in the URL
When a user types in the wrong URL or a page links to the wrong URL, URL errors can occur. Incorrect URLs cause a 404 status code because they direct users to nonexistent pages.
Page removal
When a page has a status code of 404, it indicates that the page has been removed, either purposefully or by accident.
How to Fix 404 Errors
The first step is to list every URL on the website that a search engine can find and that returns a 404 error. Two tools can help you with this: running crawling tools like DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, and others through your website, and the Coverage report in Google Search Console. Once you’ve compiled a list of these URLs, try to determine whether the problem is with the URL itself or whether the page has been removed. This step is crucial because it will show you what needs to be fixed.
Fixing Linking Errors
One of your website’s links may be broken. Broken links can be time-consuming to find on a website. DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, and others can find broken links quickly. Once identified, you can fix the linking errors easily.
Fixing Missing Pages
If some website pages were accidentally or purposefully removed, they can be restored in two ways:
1) Restore the pages
If a significant page was accidentally deleted, reinstate it and request re-indexing in Google Search Console. You could also make sitemap updates. After this, validate 404 URLs in Search Console.
2) Redirect to the most relevant page
You should reroute it to the page on your website that is most closely related if the pages that return the 404 error are unimportant. Consider a web store. If a page is removed, it should redirect to the product category page.
The homepage URL (https://www.example.com/home) shouldn’t redirect to a 404 product URL (https://www.example.com/category/product-name).
What Is a Soft 404 Error?
A soft 404 error happens when a page that is missing from the server returns. When requested, it provides the 200 status code rather than the 404 one. This tells search engine crawlers that the page is there, allowing them to browse through it even though it doesn’t exist. Worst case, they may be indexed. But because it wastes money from the crawl budget, this should be avoided at all costs.
A server can’t send the HTTP response code Soft 404 when a Web page is requested. It is merely a label that Google applies to websites that it has found. The coverage section of the Google Search Console is where you can locate soft 404 pages on your website.
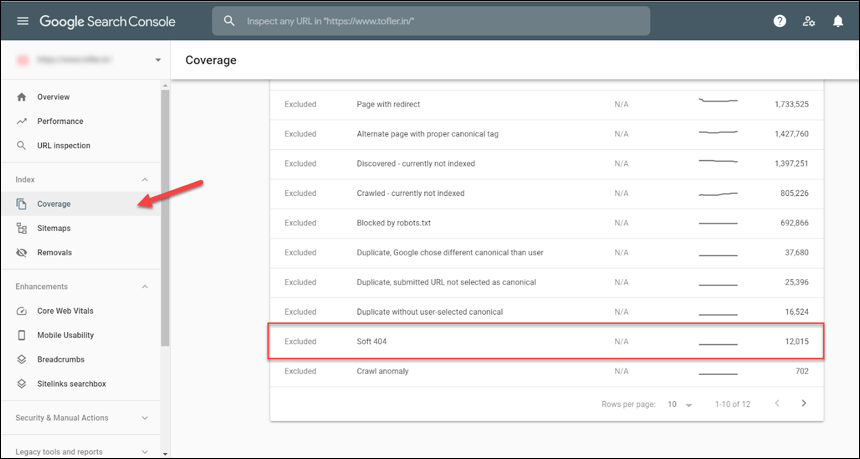
Soft 404 error happens when:
Poor server configuration
Even missing pages can return the 200 status code due to subpar server configuration, and misleading crawlers. Servers should respond to requests for missing pages with 404.
Pages with very less or no content
Sometimes live pages with very little or no content are mistakenly classified as “soft 404s” because Google interprets their behavior as a page with no potential and must be a 404. These pages are categorized as “soft 404s” because Google is unsure about them.
Issues with page rendering
There’s a good chance Googlebot can’t load the page resources if your rendered page is blank or nearly blank. This may occur if the resources are very large or difficult to access. It’s called a “soft 404” because Google isn’t sure if the page is a 404 or not.
How To Fix Soft 404 Errors
In the coverage report from Search Console’s Soft 404 section, you should first extract all the URLs. Use a crawling tool to find the URLs that the 404 error meaning actually refers to out of all the URLs. Use the techniques listed in the previous section to fix these URLs. Now, follow these steps to fix the soft 404 error that happens when:
Serve correct status codes
Make sure the servers serve the appropriate status code for each and every URL, as the title suggests. A page should return a status code of 200 if it is valid, 404 if it is missing, and 301 or 302 if it has been redirected. Do not fool Googlebot!
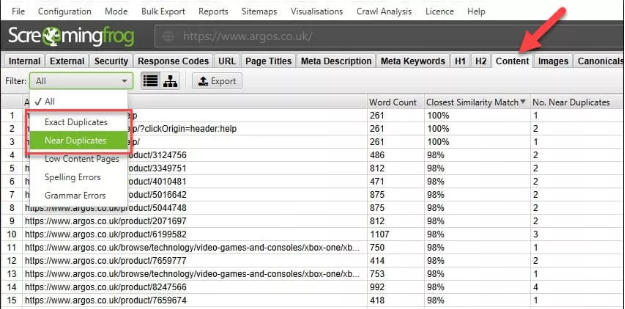
Find and fix pages with duplicate or thin content
Bypassing the soft 404 URLs through the Screaming Frog tool, it is possible to extract the word count of the content on each page. This will help you find any pages on your website that don’t have much to say. Screaming Frog also helps you identify pages with near-duplicate and exact duplicate content.
At this point, the redundancy should have been eliminated. You can add new content to them or combine pages with related topics into one page.
Technical issues that cause duplication include the resolution of URLs with or without a trailing slash, a www or non-www prefix, an HTTPS or HTTP prefix, or a URL with or without a “.html” suffix. Exist duplicate URLs with properly defined canonicals, if not? If these problems aren’t fixed, they could lead to serious problems with duplication, which is bad.
Ensure Googlebot is able to render your pages
It’s possible that the crawlers are unable to efficiently crawl or render your pages if they have sufficient content but are still marked as “soft 404.” Check the rendered screenshot and HTML in the Search Console for such URLs. If the screenshot is blank or almost blank, the pages have a problem with how they look. You can examine the rendered HTML to identify the resources that are causing problems. Make sure that crawlers have access to all resources, and avoid making them too big.
Key Takeaways
The terms “404 page” and “soft 404 error” are not interchangeable. It is a sign that there is a problem with the page because the crawlers do not regard it as a trustworthy page. But just like 404 pages, if you do not address soft 404 errors right away, Google may begin deindexing your pages, which could reduce traffic to your website if they are crucial pages. The best practice is to run a crawling tool over your website frequently to look for 404 and thin pages. You need a crawling tool, like Screaming Frog, to help you fix these errors. Screaming Frog is one of the best and most recommended options.